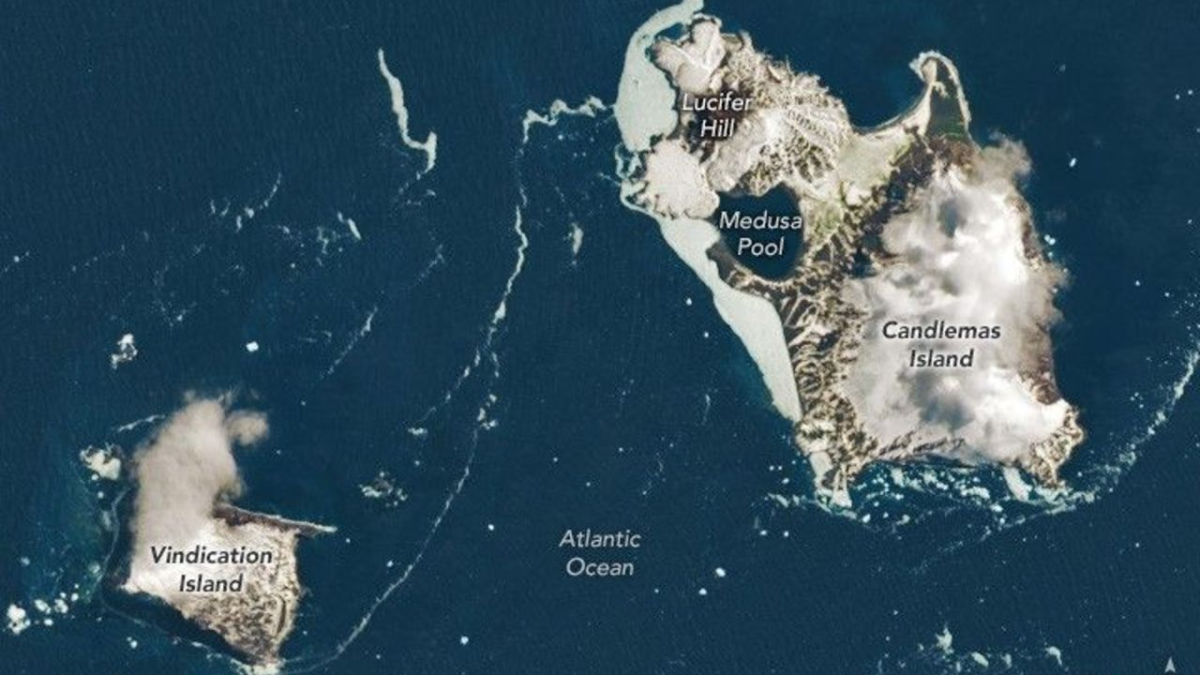
Located far from major shipping routes and human settlements, the South Sandwich Islands represent one of the planet's most secluded archipelagos. Situated in the turbulent South Atlantic Ocean, this chain lies over 1,600 kilometers from both the Antarctic continent and South America. A recent satellite photograph, acquired by the Landsat 9 spacecraft's Operational Land Imager-2, provides an unusual glimpse of Vindication and Candlemas Islands, where patches of low cloud interact with dramatic volcanic landscapes and frozen coasts.
Historical Context and Scientific Importance
Following Captain James Cook's initial sighting of two proximate islands in 1775, which were later named Candlemas and Vindication, direct exploration of this area has been extremely limited. Thick cloud layers, violent ocean conditions, and severe weather typically prevent ground-based studies. Consequently, orbital observatories have emerged as the key tool for researchers examining volcanic processes, glacial changes, coastal erosion, and atmospheric dynamics in this largely pristine setting.
Due to reduced cloud interference during this observation, the satellite could identify specific formations on Candlemas Island, such as Lucifer Hill and Medusa Pool.
Geological Evolution and Environmental Forces
Images like this enable scientists to track how volcanic landforms develop under harsh climatic conditions. Candlemas Island originally consisted of two distinct islands that fused together over hundreds of years. Its southeastern section is an ancient, heavily worn stratovolcano now covered by ice, whereas the northwestern area features more recent lava streams originating from cinder cones including Lucifer Hill. Records from the 1900s mention eruptions and steam plumes, indicating a long-standing interaction between volcanic heat and glacial ice.
The photograph also underscores the significant impact of erosion. Vindication Island displays no signs of recent volcanic action. Instead, its sheer cliffs and diminished landmass demonstrate the relentless effects of ocean waves, freezing conditions, and storms, which gradually break down volcanic structures after tectonic forces diminish.
Atmospheric Observations
The cloud formations visible are themselves scientifically valuable. The South Sandwich Islands are known for generating distinctive wave clouds, formed when powerful winds ascend over steep topography. These atmospheric features, sometimes detectable from space, offer clues about air movement and stability in distant marine regions, information that aids meteorological and climatic research.